Using jmove-api
jmove-api makes it easy to design and implement rules in the form of unit tests. As an example we want to realize such tests based on JUnit4:
Preparations
First, add jmove-api.jar specific to your build tool (ANT, Gradle, Maven, ...) to the test classpath.
Base-Class
To supply all tests the same model it is convenient to create a super class to share a single model
in the whole virtual machine. The model can be built in a simple way using JModelBuilder.
In our example we built the model from all class files found in the directory "./target/classes"
and its subdirectories.
import org.jmove.java.loader.JModelBuilder;
import org.jmove.java.model.JModel;
import org.junit.BeforeClass;
public abstract class AbstractModelTest {
private static JModel theModel = null;
@BeforeClass
public static void setUpModel() {
if (theModel == null) {
theModel = new JModelBuilder("example")
.withModule("main", "./target/classes")
.build();
}
}
}
Package cycle
Our first test checks if any package cycle in the model exists.
Package cycles are inherently evil! Package cycle are an indication for software systems with increased support
needs.
The test use a PackageCycleMonitor, which expects no further arguments, so the test is a one-liner!
public class PackageCycleTest extends AbstractModelTest {
@Test
public void noCycles() throws Exception {
Assert.noAlarm(createMonitor(PackageCycleMonitor.class));
}
}
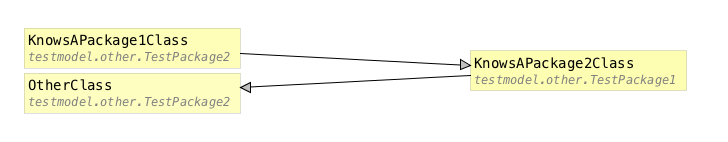
In the case no package cycle exists, everything is fine. But when a cycle exists the output shows the participating packages in the found cycles, i.e.:
java.lang.AssertionError:
[ Package cycle monitor, 1
(Package cycle monitor: Severity 9, Cyclic package dependencies
[ testmodel.other.TestPackage2 - testmodel.other.TestPackage1 ]!,
Subject '[ testmodel.other.TestPackage2 - testmodel.other.TestPackage1 ]',
Affected 'testmodel.other.TestPackage2, testmodel.other.TestPackage1')
]
To get more details about the package cycle use jmover: load your model, then the alarm tab shows the package cycle with severity 9, double-click the alarm and double-click the link between the packages to get the details. You will see the classes causing the package cycle.

Package order
The next test uses another Monitor,
but the PackageOrderMonitor expects further configuration.
It expects a list of "subpackages" and checks whether each "subpackage" depends only on "subpackages"
in the list in front of it.
In a more abstract way, this Monitor can ensure, that the tiers in your architecture are separated well.
For example the following test checks whether
- the package
my.project.domainhas no dependency tomy.project.serviceormy.project.viewand - the package
my.project.servicehas no dependency tomy.project.view.
public class PackageOrderTest extends AbstractModelTest {
@Test
public void subPackagesInCorrectDependencyOrder() throws Exception {
PackageOrderMonitor monitor = createMonitor(PackageOrderMonitor.class);
monitor.setPackageAndSubpackageOrder("my.project", new String[]{"domain", "service", "view"});
Assert.noAlarm(monitor);
}
}
Package Dependency
Apart from the offered Monitors it is of course possible to work directly with the model elements.
The following example uses these opportunities to ensure that there are no unwanted dependencies between
jmove-api and jmover in the case of jmove.
public class PackageDependencyTest extends AbstractModelTest {
@Test
public void noDependenciesToJmover() {
Set<JPackage> jmovePackages = getModel().getPackages( thing -> thing.id().startsWith("org.jmove"));
Set<JPackage> testPackages = jmovePackages.stream()
.filter(thing -> thing.id().contains("jmover"))
.collect(Collectors.toSet());
jmovePackages.removeAll(testPackages);
assertTrue(dependsOn(testPackages, jmovePackages));
Assert.noDependency( jmovePackages, testPackages );
}
}
Further Reading
To get deeper into the use of the jmove-api, Code Analysis with jmove,
API Reference and the source code examples in the package
org.jmove.examples are helpful.